
The International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD-3), created by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, has criteria for narcolepsy somewhat similar to the DSM’s. However, a doctor can find the DSM criteria for narcolepsy if a person complains of those specific symptoms. While sleep experts often know the signs of narcolepsy when they see them, most doctors are not as aware. It also gives doctors a common basis for the classification of symptoms.Īnother advantage is that it can be used by doctors who are not experts in sleep.
NARCOLEPSY WITHOUT CATAPLEXY PROFESSIONAL
With simple sorting and classifications of symptoms, it allows any medical professional to reach a tentative diagnosis. One advantage of the DSM-5 is that it is designed for clinical practice.

Neurological disorders that present physical signs in the central nervous system and also affect mental health are included. Some may assume that if a condition is in the DSM-5, that means that it doesn’t have a physical basis in the body. It also covers conditions like insomnia disorder, hypersomnolence disorder, obstructive sleep apnea, circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders, rapid eye movement (REM) sleep behavior disorder, restless legs syndrome, and medication-induced sleep disorder. The DSM-5 includes 11 diagnostic groups of sleep-wake disorders, including narcolepsy. The descriptive text describes the symptoms, other features of the condition, associated diagnoses (comorbidities) and subtypes, known prevalence of the condition, and various diagnostic measures available for the condition - if there are any. Many conditions have notes to rule out diagnoses as well these are conditions that cannot be present in a person receiving that diagnosis.ĭiagnoses are further classified into a numbered system that groups related conditions. The diagnostic criteria list the symptoms required for a diagnosis, and how long those symptoms must be present. There are three main parts: diagnostic criteria, diagnosis classification, and descriptive text. Similarly, the DSM was designed to bring together patterns of symptoms that psychiatric professionals had seen in practice and group them together in classifiable diagnoses.ĭSM-5, the most recent edition, was first published in 2013. That data can be used to study patterns from related and seemingly unrelated conditions. The DSM was inspired by the World Health Organization’s International Classification of Diseases, which is used to classify conditions by symptoms and etiology. It was first created in 1952 by the American Psychiatric Association.
NARCOLEPSY WITHOUT CATAPLEXY MANUAL
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders is a guide psychiatrists and psychologists use to classify diagnoses by symptoms.
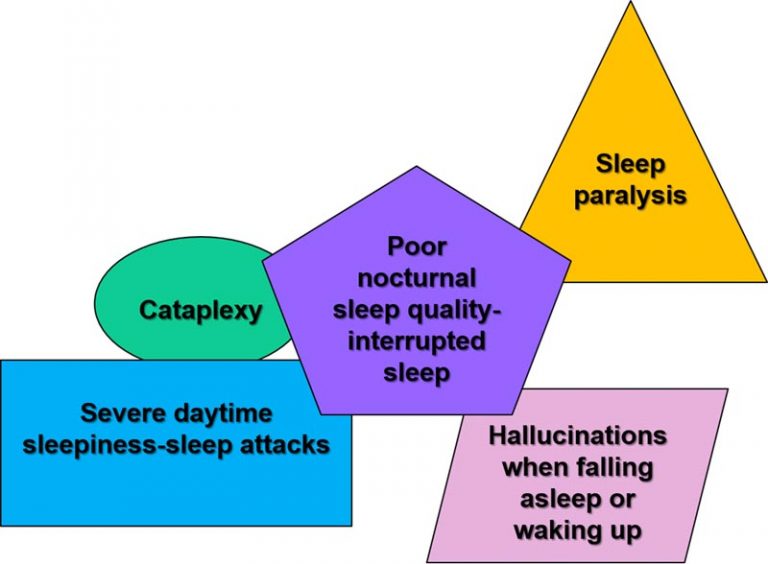
What is the DSM-5, and why are those categories there? Here’s an explanation. It’s listed under the category of sleep-wake disorders. But if you take a look in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), you’ll see narcolepsy there. Since narcolepsy is a neurological disorder, it might seem strange that it’s listed as a diagnosis in a psychiatric manual.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
